Main Objectives:
– A complete characterization of the properties of X-ray Ultra Fast Outflows (UFOs) in Narrow Line Seyfert 1 (NLSy1) Galaxies;
– To establish the contribution of local Seyfert 1 galaxies to AGN feedback through a multi-wavelength analysis (X-ray, mm and optical data).
Targets – NLSy1 with UFO:
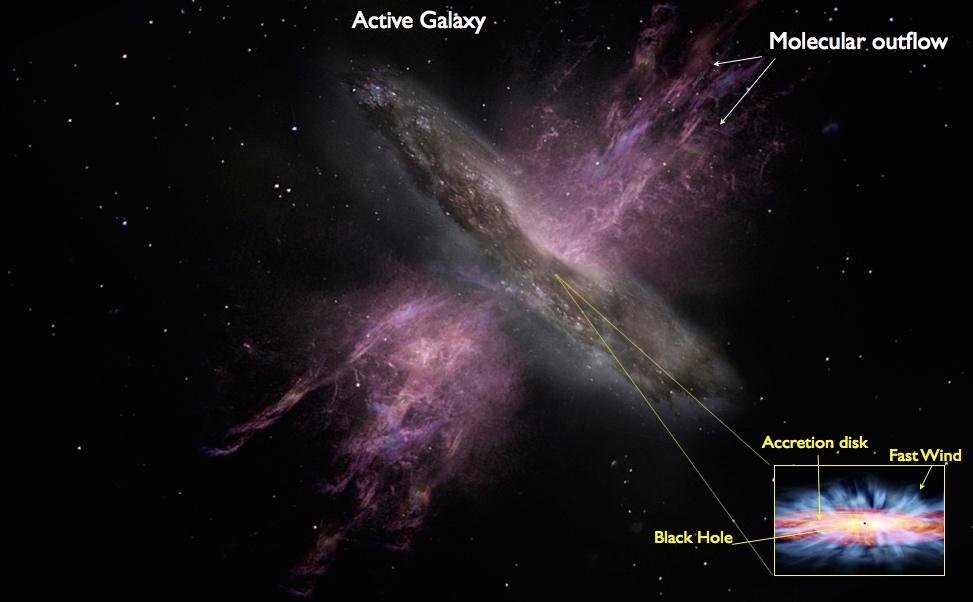
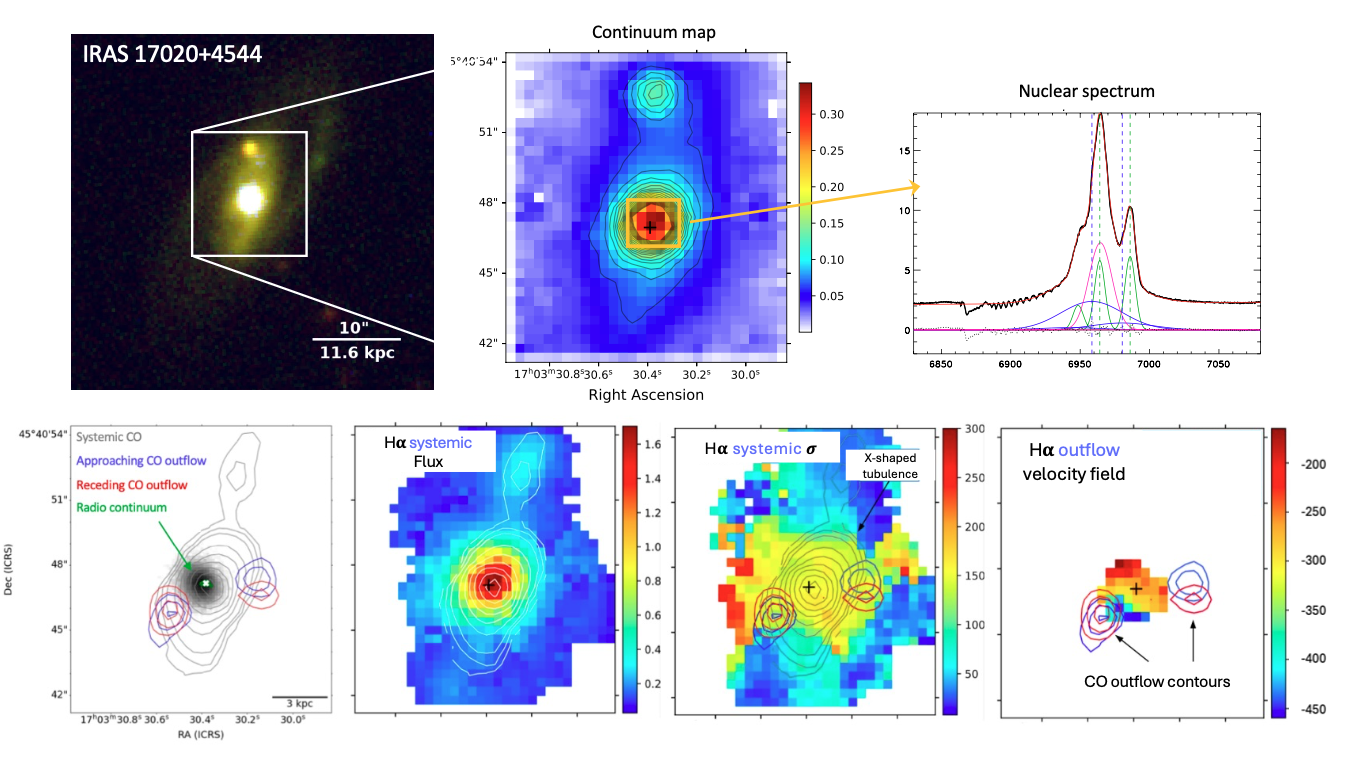
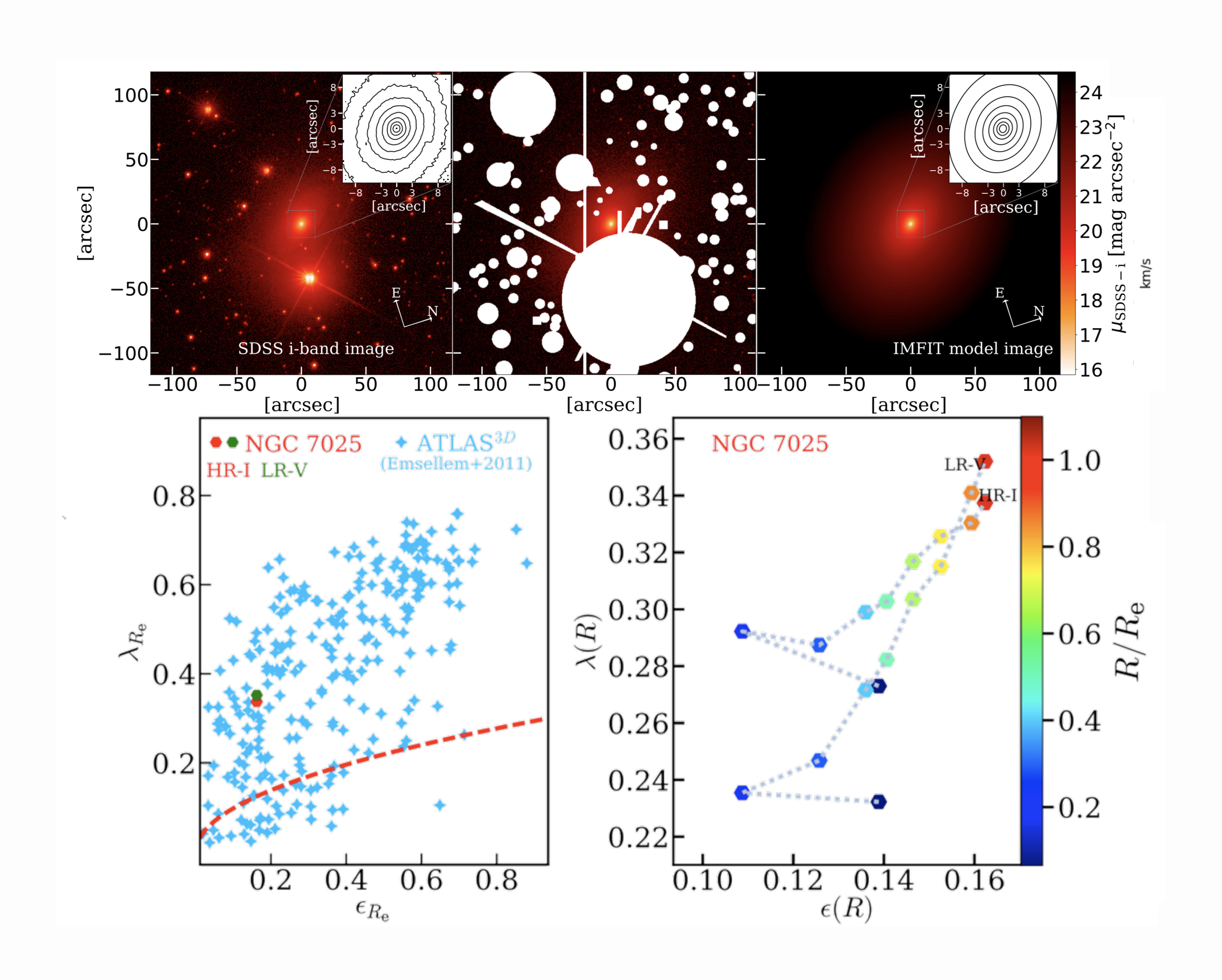
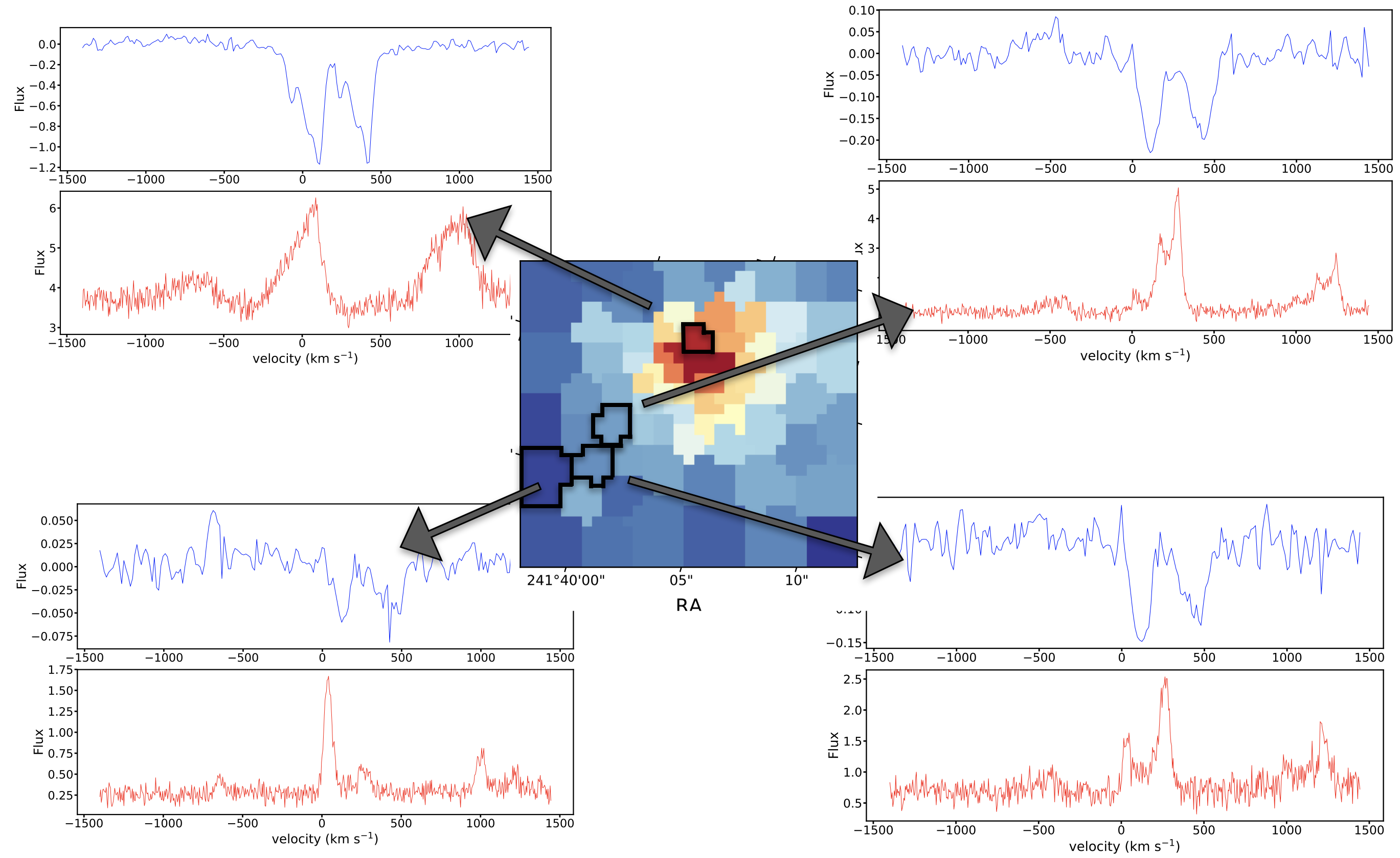
– IRAS17020+4544 was the first AGN where the detection of a multi-component X-ray UFO showed a stratified structure and IRAS17 is also the first AGN for which the presence of an energy-driven wind. For IRAS1720+4544, multi-wavelength observations, including MEGARA-IFU data, confirm galaxy-scale outflows in ionized and molecular gas linked to the X-ray UFO (Bellocchi et al., in prep);
– Ark 564 also shows a nuclear UFO in the X-ray band, and NOEMA data reveal detailed molecular gas dynamics, including systemic and outflow components.
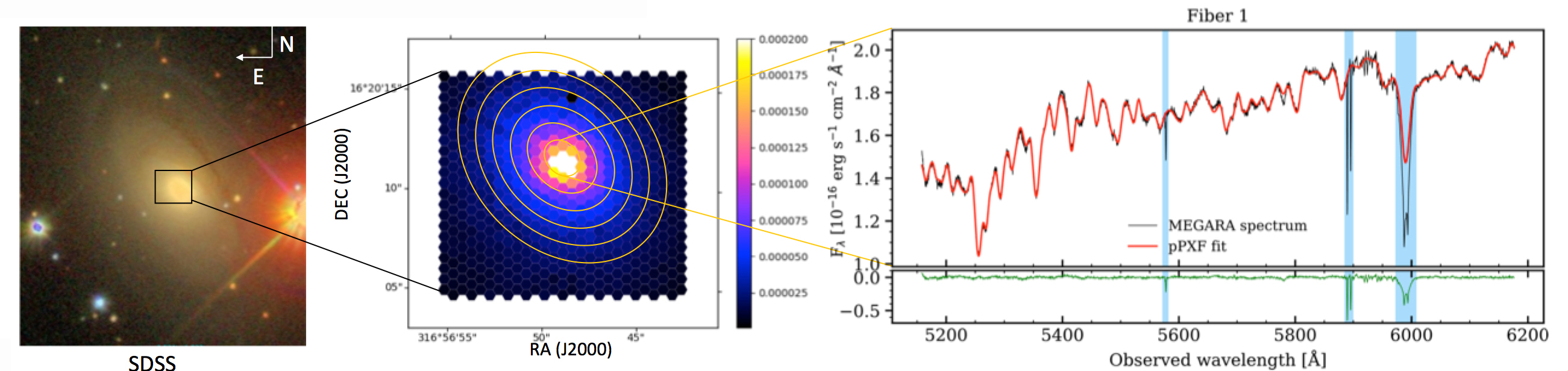
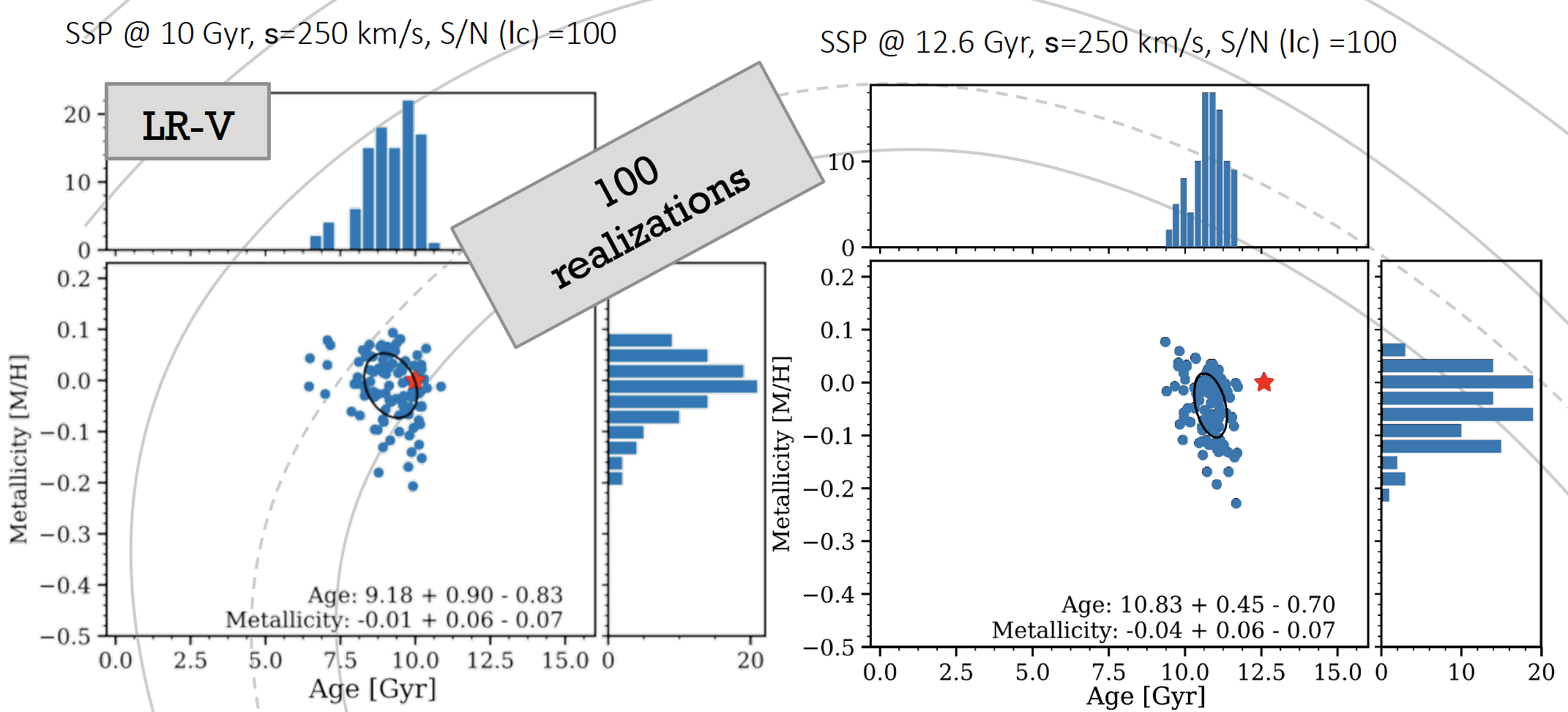
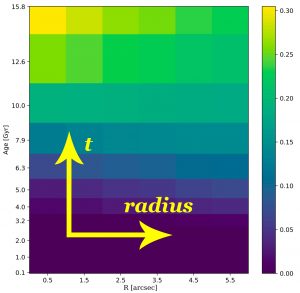
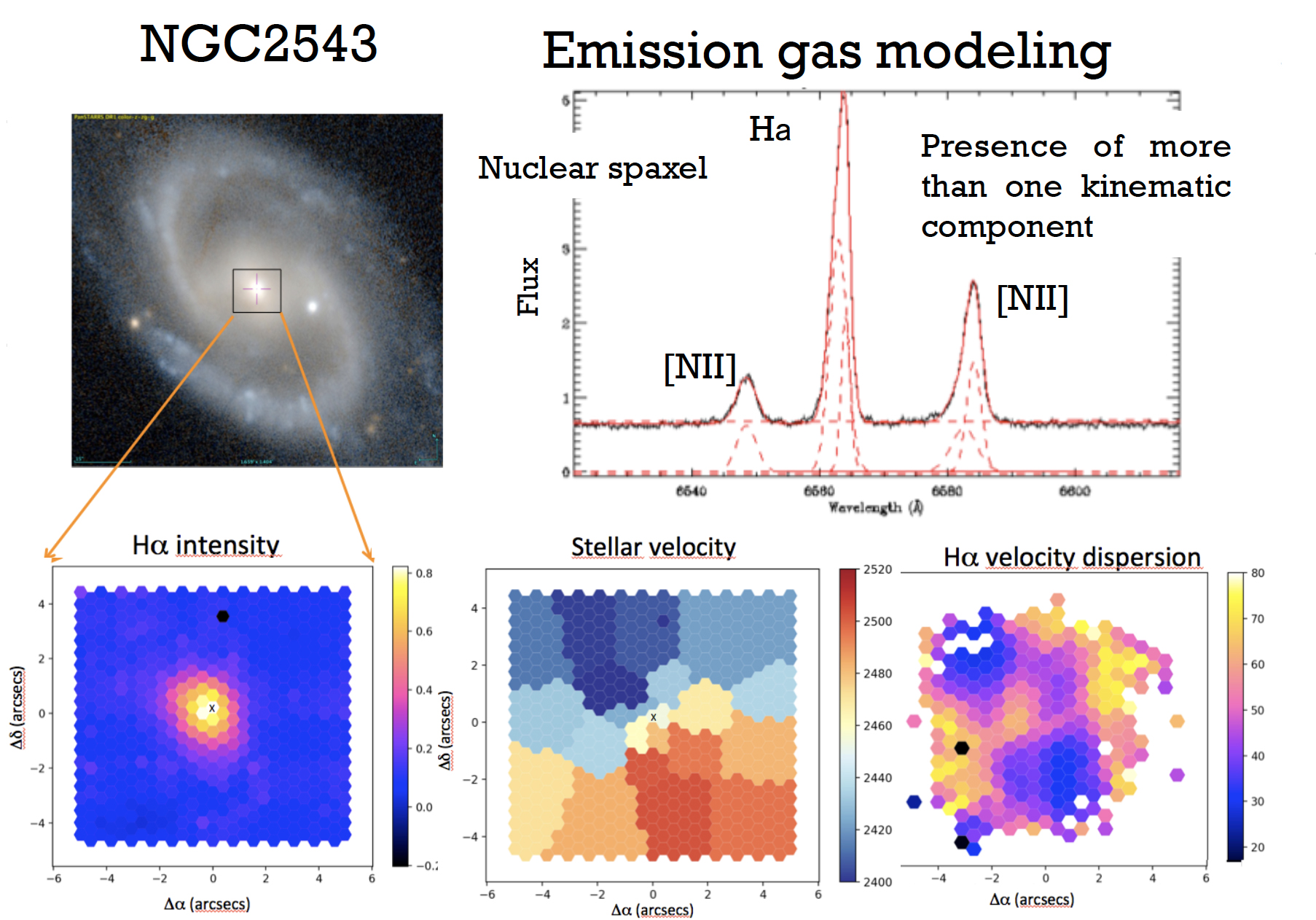
MEGARA’s capabilities provide a unique opportunity to map AGN-driven outflows of ionized gas, using a multi-component kinematic approach to analyze key emission lines like [OIII] and Hα. These observations will offer an unprecedented view of the ionized gas properties in the host galaxy and help elucidate the connection between nuclear UFOs and galaxy-scale outflows.